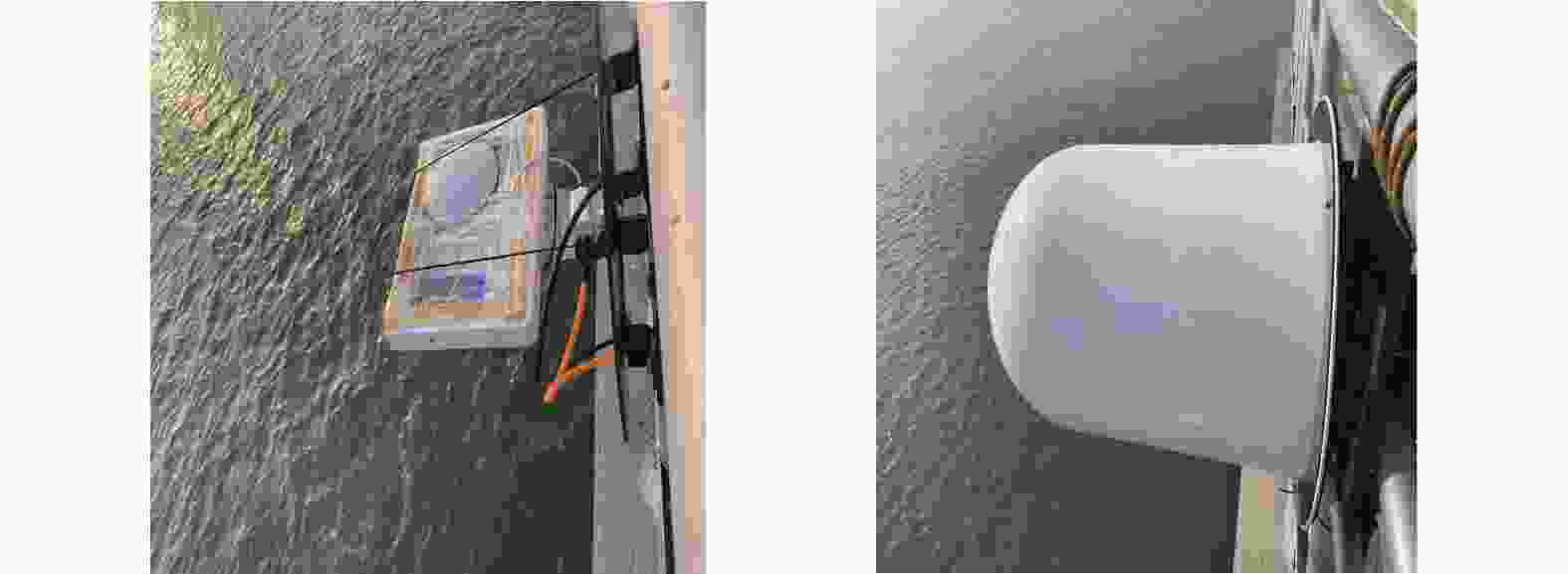
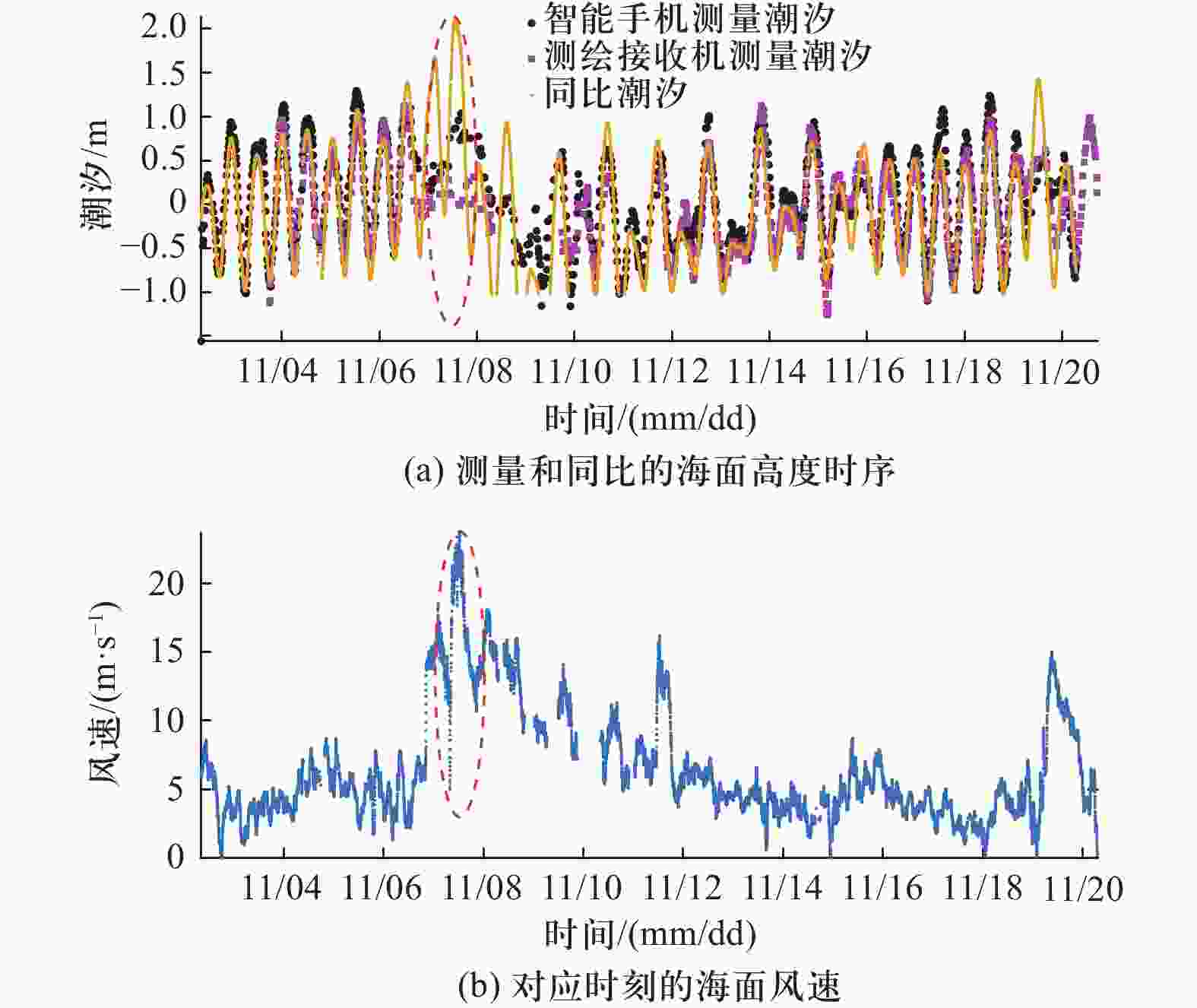
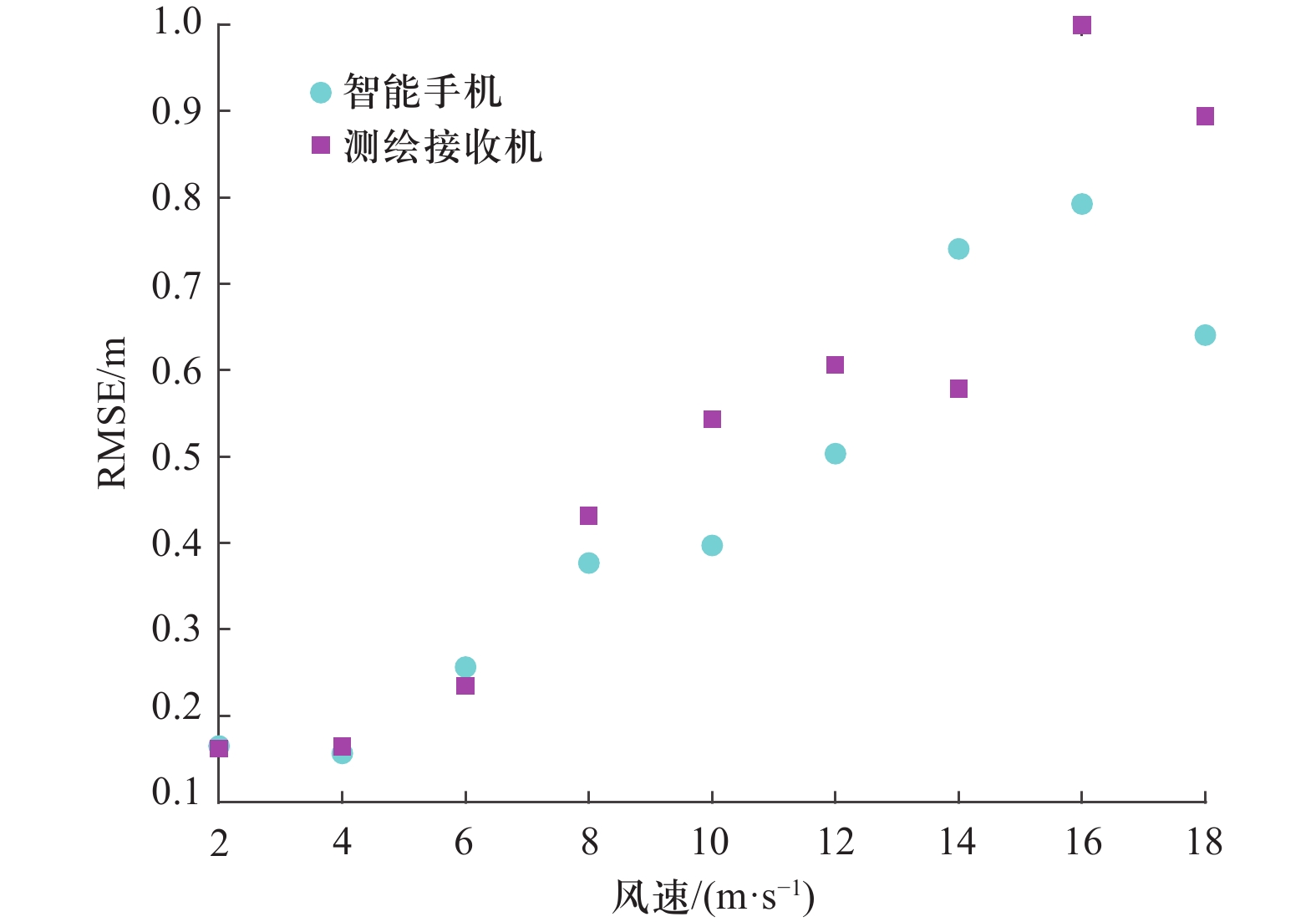
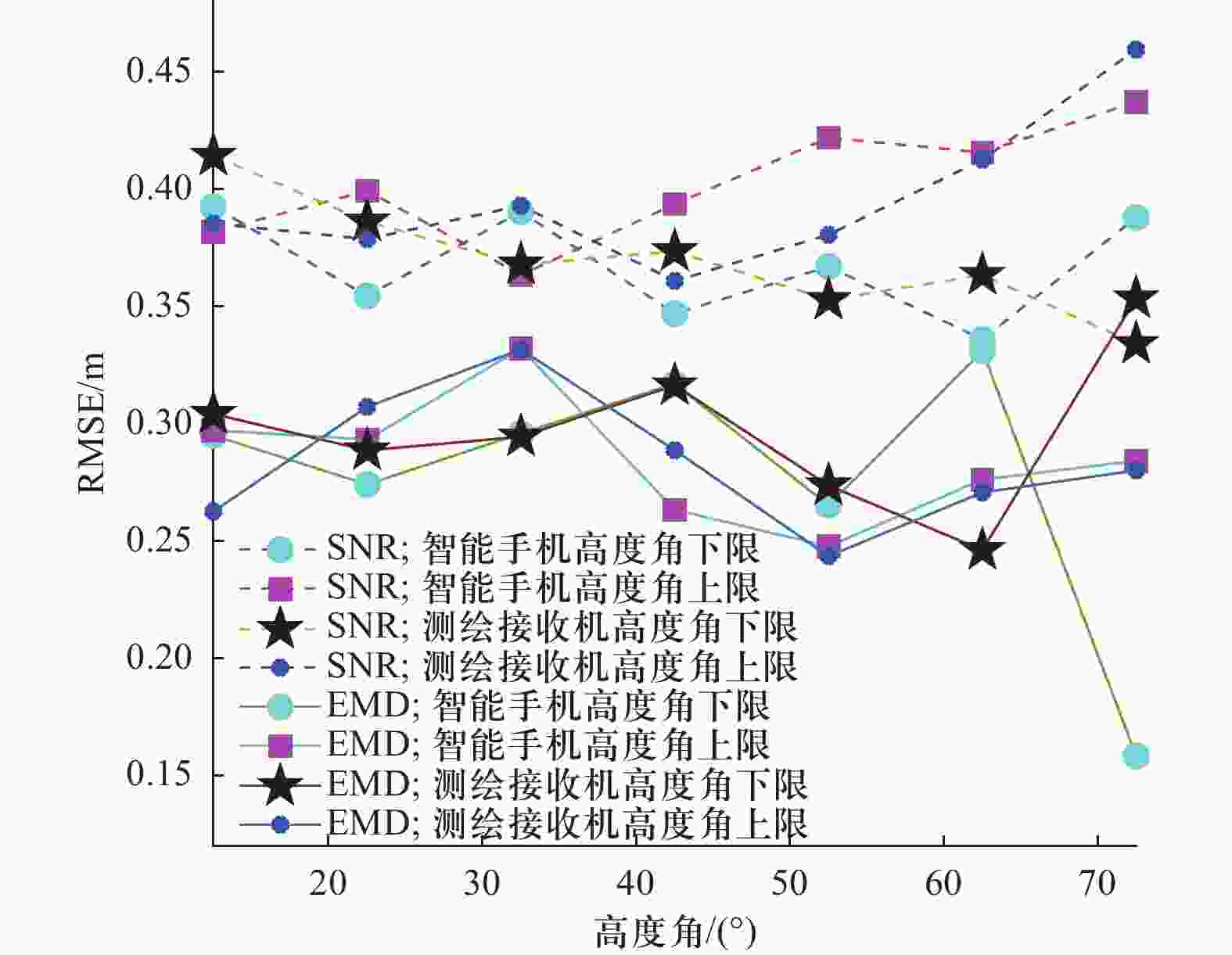
| [1] |
NEUMANN B, VAFEIDIS A, ZIMMERMANN J. Future coastal population growth and exposure to sea level rise and coastal flooding-a global assessment[J]. Plos One, 2015, 10(3): e0131375.
|
| [2] |
文汉江, 金涛勇, 朱广彬. 卫星测高原理及应用[M]. 北京: 测绘出版社, 2017.WEN Hanjiang, JIN Taoyong, ZHU Guangbin. Principle and application PF satellite altimetry[M]. Beijing: Surveying and Mapping Publishing House, 2017.(in Chinese)
|
| [3] |
米银霞. 卫星雷达高度计的海洋参数反演与近海重跟踪算法研究[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2019.MI Yinxia. The study on ocean parameter inversion and offshore retracking based on satellite radar altimeter[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2019. (in Chinese)
|
| [4] |
王强, 杨东凯, 修春娣, 等. 基于SVM的GNSS-R探测有效波高方法[J]. bob手机在线登陆学报, 2019, 39(增刊 2): 24 − 28.WANG Qiang, YANG Dongkai, XIU Chundi, et al. Significant wave height retrieval method based on support vector machine using gnss reflected signals[J]. Transations of Beijing Institute of Technology, 2019, 39(suppl 2): 24 − 28. (in Chinese)
|
| [5] |
洪学宝, 张波, 杨东凯, 等. 地基GNSS-R功率测量应用中的天线方向性影响分析[J]. bob手机在线登陆学报, 2021, 41(6): 658 − 664.HONG Xuebao, ZHANG Bo, YANG Dongkai, et al. Antenna directivity effect analysis for ground-based gnss-r power measurement application[J]. Transactions of Beijing Institute of Technology, 2021, 41(6): 658 − 664. (in Chinese)
|
| [6] |
李惟, 朱云龙, 王峰. GNSS多径信号模型及测高方法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2018, 44(6): 1239 − 1245.LI Wei, ZHUN Yunlong, WANG Feng. GNSS multipath signal model and altimetry method[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2018, 44(6): 1239 − 1245. (in Chinese)
|
| [7] |
王笑蕾, 何秀凤, 陈殊, 等. 地基 GNSS-IR风速反演原理及方法初探[J]. 测绘学报, 2021, 50(10): 1298 − 1307.doi:10.11947/j.AGCS.2021.20200586WANG Xiaolei, HE Xiufeng, CHEN Shu. et. al. Preliminary study on theory and method of ground-based GNSS-IR wind speed[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2021, 50(10): 1298 − 1307. (in Chinese)doi:10.11947/j.AGCS.2021.20200586
|
| [8] |
ROGGENBUCK O, REINKING J, LAMBERTUS T. Determination of significant wave heights using damping coefficients of attenuated GNSS SNR data from static and kinematic observations[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11: 409.
|
| [9] |
STRANDBERG J, HOBIGER T, HAAS R. Coastal sea ice detection using ground-based GNSS-R[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 14(9): 1552 − 1556.
|
| [10] |
汉牟田, 张波, 杨东凯, 等. 利用GNSS干涉信号振荡幅度反演土壤湿度[J]. 测绘学报, 2016, 45(11): 1293 − 1300.doi:10.11947/j.AGCS.2016.20160145HAN Moutian, ZHANG Bo, YANG Dongkai, et al. Soil moisture retrieval utilizing GNSS interference signal amplitude[J]. Acta Geodaetica ET Cartographica Sinica, 2016, 45(11): 1293 − 1300. (in Chinese)doi:10.11947/j.AGCS.2016.20160145
|
| [11] |
LARSON K M, SMALL E E. Normalized microwave reflection index: a vegetation measurement derived from GPS networks[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2014, 7(5): 1501 − 1511.doi:10.1109/JSTARS.2014.2300116
|
| [12] |
少锋, 周威, 刘立龙, 等. 小波变换与滑动窗口相结合的GNSS-I雪深估测模型[J]. 测绘学报, 2020, 49(9): 1179 − 1188.doi:10.11947/j.AGCS.2020.20200268SHAO Feng, ZHOU Wei, LIU Lilong, et. al. GNSS-IR model of snow depth estimation combining wavelet transform with sliding window[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2020, 49(9): 1179 − 1188. (in Chinese)doi:10.11947/j.AGCS.2020.20200268
|
| [13] |
STRANDERG J, HOBIGER T, HASS R. Real-time sea-level monitoring using Kalman filtering of GNSS data[J]. GPS Solutions, 2019, 23: 61.
|
| [14] |
何秀凤, 王杰, 王笑蕾, 等. 利用多模多频GNSS-IR 信号反演沿海台风风暴潮[J]. 测绘学报, 2020, 49(9): 1168 − 1178.HE Xiufeng, WANG Jie, WANG Xiaolei, et. al Retrieval of coastal typhoon storm surge using Multi-GNSS-IR[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2020, 49(9): 1168 − 1178. (in Chinese)
|
| [15] |
KIM S K, PARK J. Monitoring a storm surge during hurricane Harvey using multi-constellation GNSS-Reflectometry[J]. GPS Solutions, 2021, 25(2): 63.doi:10.1007/s10291-021-01105-2
|
| [16] |
FAGUNDES M R R, TMENDOCA-TINTI I, IESCHECK A K, et al. An open-source low-cost sensor for SNR-based GNS reflectometry: design and long-term validation towards sea-level altimetry[J]. GPS Solutions, 2021, 25: 73.
|
| [17] |
PURNELL D J, GOMES N, MINARIK W, et al. Precise water level measurements using low-cost GNSS antenna arrays[J]. Earth Surface Dynamics, 2021, 9: 673 − 685.
|
| [18] |
MALKOS S. User location takes center in new android OS: Google to provide raw GNSS measurement[J]. GPS World, 2016, 27(7): 36.
|
| [19] |
高成发, 陈波, 刘永胜. Android智能手机GNSS高精度实时动态定位[J]. 测绘学报, 2021, 50(1): 18 − 26.doi:10.11947/j.AGCS.2020.20200107GAO Chengfa, CHEN Bo, LIU Yongsheng. Android smartphone GNSS high-precision real-time dynamic positioning[J]. Acta Geodaetica ET Cartographica Sinica, 2021, 50(1): 18 − 26. (in Chinese)doi:10.11947/j.AGCS.2020.20200107
|
| [20] |
ALTUNTA C, TUNALIOGLU N. Feasibility of retrieving effective reflector height using GNSS-IR from a single-frequency android smartphone SNR data[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2021, 112(1): 103011.
|
| [21] |
KURUM M, FARHAD M M, GURBUZ A C. Integration of smartphones into small unmanned aircraft systems to sense water in soil by using reflected GPS signals[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2020, 14: 1048 − 1059.
|
| [22] |
徐平, 郝旺身. 振动信号处理与数据分析[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2016,:164 − 170.XU Ping, HAO Wangshen. Vibration signal processing and data analysis[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2016: 164 − 170. (in Chinese)
|
| [23] |
RODRIGUEZ-ALGVAREZ N, BOSCH-LLUIS X, CAMPS A, et al. Review of crop growth and soil moisture monitoring from a ground-based instrument implementing the interference pattern GNSS-R Technique[J]. Radio Science, 2021, 46: RS0C03.
|
| [24] |
RODRIGUEZ-ALGVAREZ N, CAMPS A, VALL-LLOSSERA M, et al. Land geophysical parameters retrieval using the interference pattern GNSS-R technique[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(1): 71 − 84.
|
| [25] |
ARROYO A A, CAMPS A, AGUASCA A, et al. Dual-polarization GNSS-R Interference pattern technique for soil moisture mapping[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2014, 7(5): 1533 − 1544.doi:10.1109/JSTARS.2014.2320792
|
| [26] |
CHEN Q, WON D, AKOS D M, Snow depth sensing using the GPS L2C signal with a dipole antenna[J]. EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing, 2014, 2014: 106.
|
| [27] |
CHEN Q, WON D, AKOS D M. Snow depth estimation accuracy using a dual-interface GPS-IR model with experimental results[J]. GPS Solutions, 2017, 21: 211 − 233.doi:10.1007/s10291-016-0517-1
|
| [28] |
卫征. 大众空间信息应用与数字经济发展[J]. 卫星应用, 2019, 5: 15 − 20.doi:10.3969/j.issn.1674-9030.2019.12.007WEI Zheng. Application of general spatial information and development of digital economy[J]. Satellite Application, 2019, 5: 15 − 20. (in Chinese)doi:10.3969/j.issn.1674-9030.2019.12.007
|
| [29] |
单杰. 从专业遥感到大众遥感[J]. 测绘学报, 2017, 46(10): 1434 − 1446.doi:10.11947/j.AGCS.2017.20170361SHAN Jie. Remote sensing: from trained professional to general public[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2017, 46(10): 1434 − 1446. (in Chinese)doi:10.11947/j.AGCS.2017.20170361
|





 下载:
下载: