Latest Accepted have been peer-reviewed and accepted, which are not yet assigned to volumes /issues, but are citable by Digital Object Identifier (DOI).
Display Method:
Display Method:
2023, 43(2): 111-117.
doi:10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2022.048
Abstract:
In order to improve the safety of oil production, the explosion suppression effect of N2and CO2under the condition of high temperature and high pressure in the wellbore needs to be studied. At present, there are few studies on the effect of different volume fractions of N2and CO2on the explosion characteristics of a fixed ratio of combustible gas to oxygen under high temperature and high pressure conditions. At 40 °C, the initial pressure of 0.5, 1.0 and 2.0 MPa, the time for CH4/C2H6/C3H8mixture to reach the maximum explosion overpressure, the maximum explosion overpressure and the deflagration indexKGunder different N2and CO2volume fractions were studied and analyzed. The effects of different initial pressures and two types of inert gases on the explosion characteristic parameters were investigated. The test results show that the inerting mechanisms of N2and CO2are the same under different initial pressures; the inerting effect of CO2is better than that of N2and has the optimal point. Before this point, the inerting effect of CO2is gradually stronger than that of N2, and the chemical effect is dominant, after this point the chemical action reaches its maximum effect, so the inerting effect of CO2is still stronger than that of N2, but the advantage is gradually reduced.
In order to improve the safety of oil production, the explosion suppression effect of N2and CO2under the condition of high temperature and high pressure in the wellbore needs to be studied. At present, there are few studies on the effect of different volume fractions of N2and CO2on the explosion characteristics of a fixed ratio of combustible gas to oxygen under high temperature and high pressure conditions. At 40 °C, the initial pressure of 0.5, 1.0 and 2.0 MPa, the time for CH4/C2H6/C3H8mixture to reach the maximum explosion overpressure, the maximum explosion overpressure and the deflagration indexKGunder different N2and CO2volume fractions were studied and analyzed. The effects of different initial pressures and two types of inert gases on the explosion characteristic parameters were investigated. The test results show that the inerting mechanisms of N2and CO2are the same under different initial pressures; the inerting effect of CO2is better than that of N2and has the optimal point. Before this point, the inerting effect of CO2is gradually stronger than that of N2, and the chemical effect is dominant, after this point the chemical action reaches its maximum effect, so the inerting effect of CO2is still stronger than that of N2, but the advantage is gradually reduced.
2023, 43(2): 118-125.
doi:10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2022.047
Abstract:
Aiming at the reliability and safety problems of low firing rate and hidden dangers of UXO at large incident angle of active small caliber projectile fuze, the response characteristics of firing mechanism of small caliber projectile impact fuze were studied. In this paper, the dynamic model of the firing mechanism with large incident angle was established, and the simple criterion of the action of the firing mechanism was obtained. Based on the numerical simulation method, the dynamic response process of the firing mechanism with large incident angle under multiple working conditions, including different impact speeds, incident angles, rolling angles and target plate thicknesses, was simulated. The effectiveness of the numerical model was verified by shooting tests. The analysis results show that the random rolling angle of the hitting ball is one of the important factors affecting the functional reliability of the firing mechanism when hitting the target at a large incident angle; the smaller the amplitude of the counter impact force, the slower the response time of the axial resultant force, which is unfavorable to the reliable function of the firing mechanism. Meanwhile, it is found that with the increase of the incident angle of the fuze and the thickness of the target plate, the failure mode of “jamming” of the guide sleeve and the firing pin appears.
Aiming at the reliability and safety problems of low firing rate and hidden dangers of UXO at large incident angle of active small caliber projectile fuze, the response characteristics of firing mechanism of small caliber projectile impact fuze were studied. In this paper, the dynamic model of the firing mechanism with large incident angle was established, and the simple criterion of the action of the firing mechanism was obtained. Based on the numerical simulation method, the dynamic response process of the firing mechanism with large incident angle under multiple working conditions, including different impact speeds, incident angles, rolling angles and target plate thicknesses, was simulated. The effectiveness of the numerical model was verified by shooting tests. The analysis results show that the random rolling angle of the hitting ball is one of the important factors affecting the functional reliability of the firing mechanism when hitting the target at a large incident angle; the smaller the amplitude of the counter impact force, the slower the response time of the axial resultant force, which is unfavorable to the reliable function of the firing mechanism. Meanwhile, it is found that with the increase of the incident angle of the fuze and the thickness of the target plate, the failure mode of “jamming” of the guide sleeve and the firing pin appears.
2023, 43(2): 126-134.
doi:10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2022.054
Abstract:
In order to analyze the physical and mechanical properties of water-cooled high temperature rock under cyclic loading, uniaxial compression and cyclic loading tests were carried out on granite, marble and sandstone specimens respectively. The results show that when the heating temperature exceeds 400 °C, the volume growth rate of the three types of rocks increases significantly, thus 400 °C can be taken as the threshold temperature for the sudden change of physical parameters of the three types of rocks. In general, the uniaxial compressive strength of three types of water-cooled high temperature rocks decreases with the increase of temperature, however the peak strength of the 200 °C granite is higher than that at room temperature. Under cyclic load, the hysteretic curve of granite is approximately linear with a larger high limit stress and lesser irreversible deformation; while for green sandstone and marble samples, the high limit stress is lower than that of the granite sample with a larger deformation. With the increase of the cyclic number, the plastic deformation of the three types of rock decrease, the elastic modulus increase, and the strength of the rocks increases then that under uniaxial compression; with temperature increases, the cracks on the failure surface are more developed, and the broken rock are more finely broken.
In order to analyze the physical and mechanical properties of water-cooled high temperature rock under cyclic loading, uniaxial compression and cyclic loading tests were carried out on granite, marble and sandstone specimens respectively. The results show that when the heating temperature exceeds 400 °C, the volume growth rate of the three types of rocks increases significantly, thus 400 °C can be taken as the threshold temperature for the sudden change of physical parameters of the three types of rocks. In general, the uniaxial compressive strength of three types of water-cooled high temperature rocks decreases with the increase of temperature, however the peak strength of the 200 °C granite is higher than that at room temperature. Under cyclic load, the hysteretic curve of granite is approximately linear with a larger high limit stress and lesser irreversible deformation; while for green sandstone and marble samples, the high limit stress is lower than that of the granite sample with a larger deformation. With the increase of the cyclic number, the plastic deformation of the three types of rock decrease, the elastic modulus increase, and the strength of the rocks increases then that under uniaxial compression; with temperature increases, the cracks on the failure surface are more developed, and the broken rock are more finely broken.
2023, 43(2): 135-142.
doi:10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2022.039
Abstract:
To study the altitude effects on the diesel combustion process under cold-start condition, the thermodynamic state of the diesel engine cylinder was simulated in a constant volume combustion chamber under the plain condition and the 2000 m altitude condition. Flame temperature andKLfactor distribution for soot concentration characterizing were obtained by the two-color method under different conditions. Results show that the simultaneous decrease of ambient temperature and pressure can produce a coupling effect, resulting in the diesel ignition delay from 2.0 ms to 3.13 ms increasing, when the altitude increases from 0 m to 2000 m. As the altitude increases, the average flame temperature decreases during the diesel combustion process, while the local high temperature area disappears and the totalKLfactor decreases. The relationship between soot characteristics and flame temperature is affected evidently with altitude increases. With the increase of altitude and the decrease of flame temperature, the soot oxidation rate decreases in the soot oxidation dominated process and the impact of local flame temperature on local soot concentration weakens.
To study the altitude effects on the diesel combustion process under cold-start condition, the thermodynamic state of the diesel engine cylinder was simulated in a constant volume combustion chamber under the plain condition and the 2000 m altitude condition. Flame temperature andKLfactor distribution for soot concentration characterizing were obtained by the two-color method under different conditions. Results show that the simultaneous decrease of ambient temperature and pressure can produce a coupling effect, resulting in the diesel ignition delay from 2.0 ms to 3.13 ms increasing, when the altitude increases from 0 m to 2000 m. As the altitude increases, the average flame temperature decreases during the diesel combustion process, while the local high temperature area disappears and the totalKLfactor decreases. The relationship between soot characteristics and flame temperature is affected evidently with altitude increases. With the increase of altitude and the decrease of flame temperature, the soot oxidation rate decreases in the soot oxidation dominated process and the impact of local flame temperature on local soot concentration weakens.
2023, 43(2): 143-150.
doi:10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2022.045
Abstract:
Aviation vector nozzle actuators are seriously affected by the heat radiation of the engine, thus, the oil return cooling method is often used to control the temperature of the actuator components. Considering the convection and radiation between the engine and the servo valve actuator, and the heat transfer process of each component of the actuator, a thermodynamic model of the vector nozzle actuator was established based on the lumped parameter method under real working conditions. The model was used to analyze and obtain the temperature distribution law and its influencing factors of each component of the actuator during the piston in neutral position and reciprocate. The analysis results show that when the piston is in near the neutral position, the oil flow passes the cooling channel, taking away heat through heat conduction, getting better cooling effect. When the piston reciprocates, the oil continuously enters and exits the rod cavity and the rodless cavity, and the temperature of each node can reach a stable fluctuation state and be lower than the thermal equilibrium temperature of the neutral position. The temperature of each node of the actuator increases with the increase of the radiation temperature, ambient temperature and oil temperature, among which the radiation temperature of the engine brake has the most obvious influence. The cylinder barrel is directly affected by the thermal radiation of the brake. When the temperature of the brake rises from 300 °C to 400 °C, the temperature of the cylinder barrel on the left and right sides can increase by about 40 °C. Through convective heat transfer, the temperature of each node of the actuator can increase linearly with the increase of ambient temperature and oil temperature.
Aviation vector nozzle actuators are seriously affected by the heat radiation of the engine, thus, the oil return cooling method is often used to control the temperature of the actuator components. Considering the convection and radiation between the engine and the servo valve actuator, and the heat transfer process of each component of the actuator, a thermodynamic model of the vector nozzle actuator was established based on the lumped parameter method under real working conditions. The model was used to analyze and obtain the temperature distribution law and its influencing factors of each component of the actuator during the piston in neutral position and reciprocate. The analysis results show that when the piston is in near the neutral position, the oil flow passes the cooling channel, taking away heat through heat conduction, getting better cooling effect. When the piston reciprocates, the oil continuously enters and exits the rod cavity and the rodless cavity, and the temperature of each node can reach a stable fluctuation state and be lower than the thermal equilibrium temperature of the neutral position. The temperature of each node of the actuator increases with the increase of the radiation temperature, ambient temperature and oil temperature, among which the radiation temperature of the engine brake has the most obvious influence. The cylinder barrel is directly affected by the thermal radiation of the brake. When the temperature of the brake rises from 300 °C to 400 °C, the temperature of the cylinder barrel on the left and right sides can increase by about 40 °C. Through convective heat transfer, the temperature of each node of the actuator can increase linearly with the increase of ambient temperature and oil temperature.
2023, 43(2): 151-160.
doi:10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2022.109
Abstract:
In order to improve the efficiency of existing random search methods, a search strategy was proposed to reconnoiter a hidden-object of the reconnaissance mission. The strategy, called combined planning path and combined sensor search method (CP&CS), was designed mainly to be applied to unmanned ground vehicles equipped with different detection range sensors. In CP&CS, a sensor-based goaled rapidly-exploring random tree was arranged to plan the global path towards the hidden object. Besides, a heuristic A* method was utilized to deal with the narrow channel formed by obstacles. A simulation experiment was designed to validate the proposed strategy. The results show that in a simulation environment with 250 meter radius and occlusions, compared with the path deformation strategy with short-range sensors, the CP&CS method can improve the search efficiency by 3.11 times and shortens the length of planned path by 9.63%. Compared with goaled RRT search strategy with long-range sensors, the CP&CS method can improve the search efficiency by 3.53 times and shortens the length of planned path by 12.06%. The experimental results prove the superiority of the proposed CP&CS strategy in hidden-object search of reconnaissance mission.
In order to improve the efficiency of existing random search methods, a search strategy was proposed to reconnoiter a hidden-object of the reconnaissance mission. The strategy, called combined planning path and combined sensor search method (CP&CS), was designed mainly to be applied to unmanned ground vehicles equipped with different detection range sensors. In CP&CS, a sensor-based goaled rapidly-exploring random tree was arranged to plan the global path towards the hidden object. Besides, a heuristic A* method was utilized to deal with the narrow channel formed by obstacles. A simulation experiment was designed to validate the proposed strategy. The results show that in a simulation environment with 250 meter radius and occlusions, compared with the path deformation strategy with short-range sensors, the CP&CS method can improve the search efficiency by 3.11 times and shortens the length of planned path by 9.63%. Compared with goaled RRT search strategy with long-range sensors, the CP&CS method can improve the search efficiency by 3.53 times and shortens the length of planned path by 12.06%. The experimental results prove the superiority of the proposed CP&CS strategy in hidden-object search of reconnaissance mission.
2023, 43(2): 161-169.
doi:10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2022.052
Abstract:
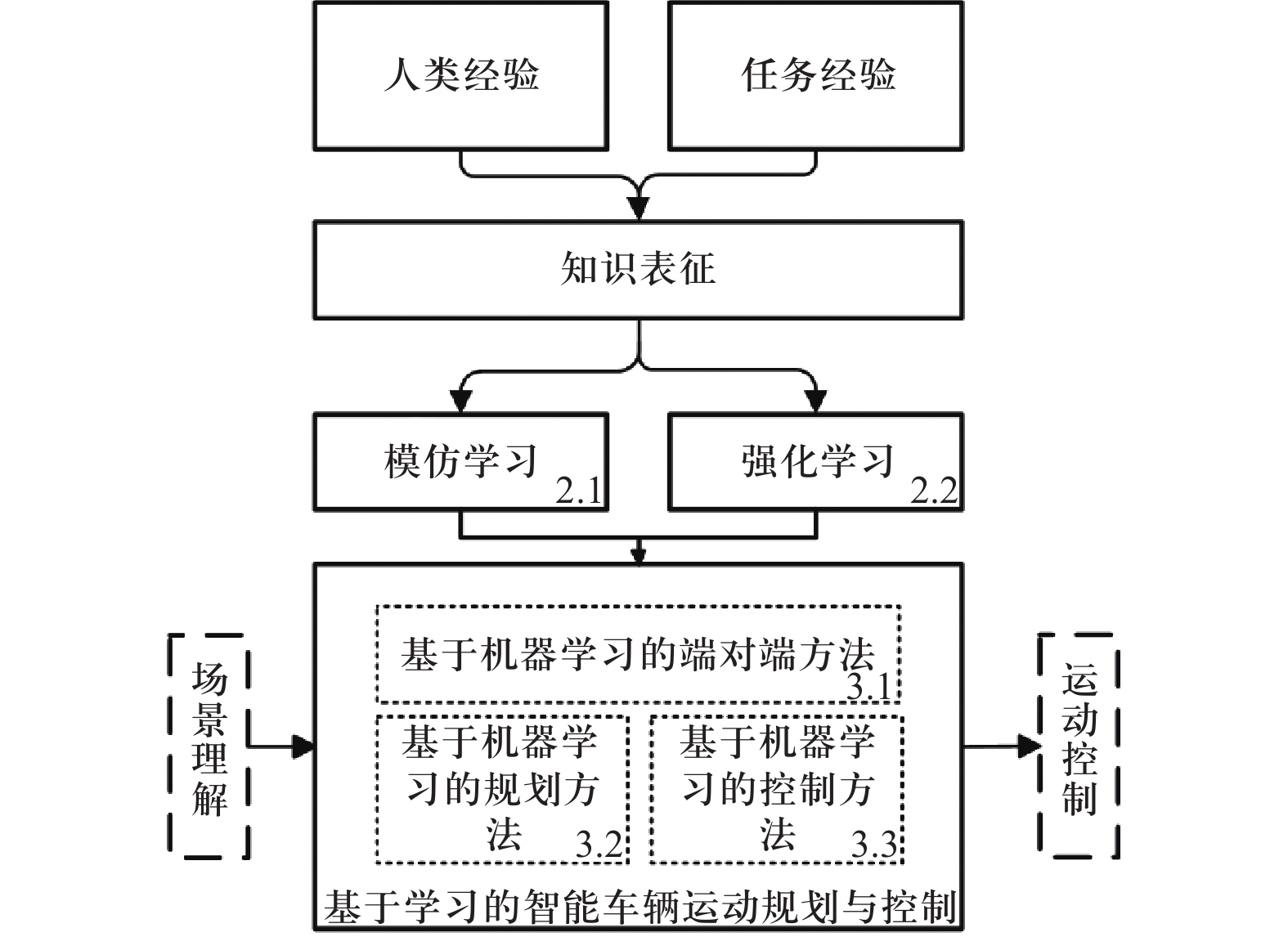
Aiming at the problem of high cost of steering system of four-wheel independent steering electric vehicle (4WIS-EV) and less functional development, a vehicle oblique driving control method was proposed to optimize the driving stability of 4WIS-EV during lane changing. Firstly, based on the 4WIS-EV lateral and longitudinal two-degree-of-freedom vehicle model, a lateral and longitudinal coupled trajectory tracking control method was proposed. According to linear-time-variant (LTV) model and model predictive control (MPC) algorithm, a closed-loop control of lateral deviation, heading angle deviation and longitudinal speed deviation was carried out. And then, a vehicle stability controller was designed, including yaw moment controller and torque distribution controller to improve trajectory tracking accuracy and driving stability simultaneously. Finally, a Simulink/Carsim/Prescan co-simulation platform was built to carry out the lane-changing simulation of the 4WIS-EV in double-line shifting condition. The simulation results show the feasibility of the oblique lane change and the effectiveness of the lateral and longitudinal coupled trajectory tracking control method.
Aiming at the problem of high cost of steering system of four-wheel independent steering electric vehicle (4WIS-EV) and less functional development, a vehicle oblique driving control method was proposed to optimize the driving stability of 4WIS-EV during lane changing. Firstly, based on the 4WIS-EV lateral and longitudinal two-degree-of-freedom vehicle model, a lateral and longitudinal coupled trajectory tracking control method was proposed. According to linear-time-variant (LTV) model and model predictive control (MPC) algorithm, a closed-loop control of lateral deviation, heading angle deviation and longitudinal speed deviation was carried out. And then, a vehicle stability controller was designed, including yaw moment controller and torque distribution controller to improve trajectory tracking accuracy and driving stability simultaneously. Finally, a Simulink/Carsim/Prescan co-simulation platform was built to carry out the lane-changing simulation of the 4WIS-EV in double-line shifting condition. The simulation results show the feasibility of the oblique lane change and the effectiveness of the lateral and longitudinal coupled trajectory tracking control method.
2023, 43(2): 170-177.
doi:10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2022.043
Abstract:
The multi-channel wireless shore power system with both parallel input and output can realize high-power transmission of ship shore power through modular superposition, and solve the problem of single-channel power limitation. However, some parameter differences and disturbances occurred in the process of module production, installation and operation will cause instability of the shore power output voltage and affect the reliable operation of the wireless shore power system. To solve this problem, a circuit topology was proposed firstly for the multi-channel parallel wireless shore power system. And then, taking the inverter phase shift angle as the input and the target load power as the output, a multi-channel parallel wireless shore power system model was established. Using a energy-phase angle method to reduce the system order, a small signal system model was established. Based on the Trapezoidal step bilinear approximation method, a system controller was designed to analyze the parameter differences of the channel coupling, DC input voltage and load disturbance separately. Finally, Matlab simulation and experiment were carried out to validate the control effect under the three disturbance conditions. The results show the better control effect of system controller, which can make a stable operation of the multi-channel shore power system. As a technical support, the proposed method is suitable for high-power wireless design and application of shore power system.
The multi-channel wireless shore power system with both parallel input and output can realize high-power transmission of ship shore power through modular superposition, and solve the problem of single-channel power limitation. However, some parameter differences and disturbances occurred in the process of module production, installation and operation will cause instability of the shore power output voltage and affect the reliable operation of the wireless shore power system. To solve this problem, a circuit topology was proposed firstly for the multi-channel parallel wireless shore power system. And then, taking the inverter phase shift angle as the input and the target load power as the output, a multi-channel parallel wireless shore power system model was established. Using a energy-phase angle method to reduce the system order, a small signal system model was established. Based on the Trapezoidal step bilinear approximation method, a system controller was designed to analyze the parameter differences of the channel coupling, DC input voltage and load disturbance separately. Finally, Matlab simulation and experiment were carried out to validate the control effect under the three disturbance conditions. The results show the better control effect of system controller, which can make a stable operation of the multi-channel shore power system. As a technical support, the proposed method is suitable for high-power wireless design and application of shore power system.
2023, 43(2): 178-186.
doi:10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2022.040
Abstract:
In order to provide quantitative basis for the selection of emergency resource mobilization cooperation mode, a three-dimensional structural model "intervention-intensity-method" was established for local government cooperation in emergency resource mobilization. Based on 4 typical cooperation modes, the means of cooperation mode selection was transformed into a multi-index group decision problem with linguistic evaluation information. Applying information processing group decision method based on binary semantic grey relational projection, a selection model was constructed for cooperation mode. According to the basic idea of the traditional projection analysis method, the relative closeness of the alternative to the positive ideal scheme was obtained by calculating the projection value of the alternative scheme to the positive ideal scheme and the negative ideal scheme, and finally the optimal scheme was determined. On the basis of theoretical research, an empirical analysis of the emergency resource mobilization cooperation model was carried out in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. The results show that the emergency resource mobilization cooperation in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region is more suitable for a strong administrative cooperation model with higher-level government intervention. Calculation results based on expert evaluation data show that this method can better reflect the matching degree between the cooperation mode and the objective situation, and play a better role in mode selection.
In order to provide quantitative basis for the selection of emergency resource mobilization cooperation mode, a three-dimensional structural model "intervention-intensity-method" was established for local government cooperation in emergency resource mobilization. Based on 4 typical cooperation modes, the means of cooperation mode selection was transformed into a multi-index group decision problem with linguistic evaluation information. Applying information processing group decision method based on binary semantic grey relational projection, a selection model was constructed for cooperation mode. According to the basic idea of the traditional projection analysis method, the relative closeness of the alternative to the positive ideal scheme was obtained by calculating the projection value of the alternative scheme to the positive ideal scheme and the negative ideal scheme, and finally the optimal scheme was determined. On the basis of theoretical research, an empirical analysis of the emergency resource mobilization cooperation model was carried out in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. The results show that the emergency resource mobilization cooperation in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region is more suitable for a strong administrative cooperation model with higher-level government intervention. Calculation results based on expert evaluation data show that this method can better reflect the matching degree between the cooperation mode and the objective situation, and play a better role in mode selection.
2023, 43(2): 187-196.
doi:10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2022.046
Abstract:
In this paper, the sea surface height measurement was explored based on Android smartphone, assessing its performance initially through comparing the measured sea surface height from Android and geodetic receiver to the data in situ. In order to weaken the influence of the signals from the non-observation areas on the measurement of sea surface height, an empirical mode decomposition (EMD) was proposed to extract the oscillation feature from the signal reflected off sea surface. And simulation and experiment were carried out to demonstrate its significance. The GNSS data collected by Xiaomi 6 smartphone and Huace BeiDou N72 geodetic receiver in 18 days were conducted to measure sea surface height and assess the performance. The experimental results show that, when wind speed is below 15 m/s, the measured sea surface heights from smartphone and geodetic receiver are agreement with in-situ ones from tide gauge, both with the root mean square error (RMSE) of 0.31 m. There are 30.8% and 45.3% lower and upper bound of the elevation angle of the GNSS signals to be over 30°, so that Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) with higher elevation angle can be used to measure sea surface height. During the experiment within 18 days, 1120 in total and 62 measurements each day are obtained, therefore, in the same measurement period, compared to CORS station, more measurements can be obtained. In addition, the remote sensing was also discussed based on smartphone to promote the practicality of generally public remote sensing.
In this paper, the sea surface height measurement was explored based on Android smartphone, assessing its performance initially through comparing the measured sea surface height from Android and geodetic receiver to the data in situ. In order to weaken the influence of the signals from the non-observation areas on the measurement of sea surface height, an empirical mode decomposition (EMD) was proposed to extract the oscillation feature from the signal reflected off sea surface. And simulation and experiment were carried out to demonstrate its significance. The GNSS data collected by Xiaomi 6 smartphone and Huace BeiDou N72 geodetic receiver in 18 days were conducted to measure sea surface height and assess the performance. The experimental results show that, when wind speed is below 15 m/s, the measured sea surface heights from smartphone and geodetic receiver are agreement with in-situ ones from tide gauge, both with the root mean square error (RMSE) of 0.31 m. There are 30.8% and 45.3% lower and upper bound of the elevation angle of the GNSS signals to be over 30°, so that Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) with higher elevation angle can be used to measure sea surface height. During the experiment within 18 days, 1120 in total and 62 measurements each day are obtained, therefore, in the same measurement period, compared to CORS station, more measurements can be obtained. In addition, the remote sensing was also discussed based on smartphone to promote the practicality of generally public remote sensing.
2023, 43(2): 197-202.
doi:10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2022.044
Abstract:
Robustness, the ability to resist uncertain disturbances, is an important index of machine learning model. The certified method based on random smoothing can certify the robustness of large and complex models. In the task of malware identification, the noise samples obtained by adding noise to all features using random smoothing algorithm may lose the malicious function. The existing certification algorithms construct the certified region according to the likelihood ratio of noise spatial distribution from large to small, causing the certified robust region small and the certified accuracy not good. So, a robust certification method was proposed based on random smoothing for malware recognition deep learning model. The method was arranged to add discrete Bernoulli noise only to the unnecessary features of malicious functions to construct a certifiable smoothing model, and to select the region with smaller likelihood ratio to construct a certified region to achieve more accurate certified robustness. Experiment results show that the average certified radius of the proposed method on three data sets is 4.37 times, 2.67 times and 2.72 times that of the comparison method. This method can provide the certified radius closer to the actual robust boundary, possessing a strong practical value in the evaluation of model robustness.
Robustness, the ability to resist uncertain disturbances, is an important index of machine learning model. The certified method based on random smoothing can certify the robustness of large and complex models. In the task of malware identification, the noise samples obtained by adding noise to all features using random smoothing algorithm may lose the malicious function. The existing certification algorithms construct the certified region according to the likelihood ratio of noise spatial distribution from large to small, causing the certified robust region small and the certified accuracy not good. So, a robust certification method was proposed based on random smoothing for malware recognition deep learning model. The method was arranged to add discrete Bernoulli noise only to the unnecessary features of malicious functions to construct a certifiable smoothing model, and to select the region with smaller likelihood ratio to construct a certified region to achieve more accurate certified robustness. Experiment results show that the average certified radius of the proposed method on three data sets is 4.37 times, 2.67 times and 2.72 times that of the comparison method. This method can provide the certified radius closer to the actual robust boundary, possessing a strong practical value in the evaluation of model robustness.
2023, 43(2): 203-212.
doi:10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2022.022
Abstract:
A multi-scale object detection method was proposed based on YOLOv4 deep learning algorithm to solve the multi-scale problem caused by the huge-scale difference between soldiers and armored vehicles, as well as object distance. The diversity of small object samples was enriched through targeted data augmentation methods input images were segmented to improve the resolution of input small objects of network, the detection results of large, medium and small objects were separated based on the feature pyramid network, and finally the detection results were matched and NMS processing was carried out to remove the redundant detection boxes, so as to achieve multi-scale object detection. The experimental results show that the average mean precision of small and medium objects is improved by 1.20% and 5.54% respectively, while the detection effect of large objects is maintained, which effectively improves the detection effect of small and medium objects.
A multi-scale object detection method was proposed based on YOLOv4 deep learning algorithm to solve the multi-scale problem caused by the huge-scale difference between soldiers and armored vehicles, as well as object distance. The diversity of small object samples was enriched through targeted data augmentation methods input images were segmented to improve the resolution of input small objects of network, the detection results of large, medium and small objects were separated based on the feature pyramid network, and finally the detection results were matched and NMS processing was carried out to remove the redundant detection boxes, so as to achieve multi-scale object detection. The experimental results show that the average mean precision of small and medium objects is improved by 1.20% and 5.54% respectively, while the detection effect of large objects is maintained, which effectively improves the detection effect of small and medium objects.
2023, 43(2): 213-220.
doi:10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2022.049
Abstract:
Overlap factor is a key factor that affects atmosphere detection of lidar system at near range. The accurate calculation of overlap factor is helpful to obtain more accurate detecting results. To this end, a simulation method was proposed based on ray-tracing technique to obtain the overlap factor of non-coaxial lidar system. Firstly, using a ZEMAX optical simulation software, the ray-tracing was carried out on the transmitter and telescope receiver loaded with mechanical structures to calculate the laser intensity distribution and the field of view (FOV) function of the telescope at a given distance. Then the ratio of the FOV-weighted laser intensity to the total intensity was calculated, obtaining the overlap value at the given distance. Finally, the full overlap profile was fitted through the overlap values at different distances. And this method was applied to simulate an overlap profile for a specific lidar system, and analyze the impact of axis displacement, optical-axis misalignment, laser divergence, the FOV of the telescope, and mechanical obstructions on the overlap profile of the system. The results show that when the deviation angle between the optical axes of the laser and the telescope is equal to half of the difference between the FOV of the telescope and the divergence angle of the laser, the overlap factor cannot reach 1 in the far-field, which puts forward higher requirements for the design and installation of the lidar system.
Overlap factor is a key factor that affects atmosphere detection of lidar system at near range. The accurate calculation of overlap factor is helpful to obtain more accurate detecting results. To this end, a simulation method was proposed based on ray-tracing technique to obtain the overlap factor of non-coaxial lidar system. Firstly, using a ZEMAX optical simulation software, the ray-tracing was carried out on the transmitter and telescope receiver loaded with mechanical structures to calculate the laser intensity distribution and the field of view (FOV) function of the telescope at a given distance. Then the ratio of the FOV-weighted laser intensity to the total intensity was calculated, obtaining the overlap value at the given distance. Finally, the full overlap profile was fitted through the overlap values at different distances. And this method was applied to simulate an overlap profile for a specific lidar system, and analyze the impact of axis displacement, optical-axis misalignment, laser divergence, the FOV of the telescope, and mechanical obstructions on the overlap profile of the system. The results show that when the deviation angle between the optical axes of the laser and the telescope is equal to half of the difference between the FOV of the telescope and the divergence angle of the laser, the overlap factor cannot reach 1 in the far-field, which puts forward higher requirements for the design and installation of the lidar system.
Online First have been peer-reviewed and accepted, which are not yet assigned to volumes/issues, but are citable by Digital Object Identifier (DOI).
monthly Founded in 1956
ISSN1001-0645
Sponsor:Ministry of industry and information technology of the people's Republic of China
Sponsored by:Beijing Institute of Technology