Nature Sciences
BIT has Made Research Progress in the Quality Evaluation of Reference-free Images.
Recently, Professor Deng Chenwei, PhD student Wang Shuigen, Professor Zhao Baojun from School of Information and Electronics of Beijing Institute of Technology(BIT), Professor Alan Bovik of the University of Texas at Austin, and Professor Guang-Bin Huang of Nanyang Technological University in Singapore have cooperated to use the two-dimensional kurtosis statistical characteristics of the transform domain to significantly improve the accuracy of image noise reference-free quality evaluation, while increasing model compatibility The results of the study were titled "Blind noisy image quality assessment using sub-band kurtosis" and were published in the top journal American Society of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Control Transactions [IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 50 (3) 1146-1156 (2020)] Factor IF: 10.387).
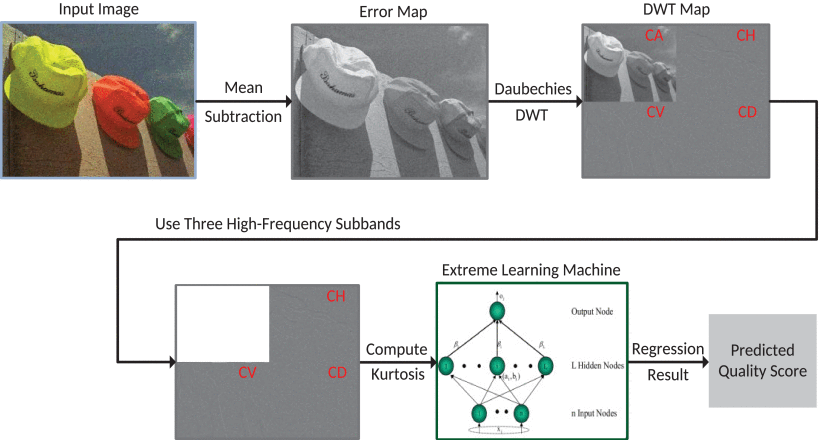
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the image quality evaluation algorithm without reference
During the acquisition, storage and transmission of digital images, noise may be introduced, resulting in a decline in image quality, making it difficult to meet user application needs. Therefore, how to accurately assess the quality of the image has become a hot spot in the field of image processing research. Image quality evaluation methods can be divided into subjective evaluation methods and objective evaluation methods. Subjective evaluation requires multiple observers to score the image, which takes time and effort.Objective evaluation is to establish a mathematical model related to image quality and let the computer automatically derive the image quality ,which can be widely used in image or video processing systems. The reference-free image quality evaluation is an objective quality evaluation method, which does not require any original image information, but only relies on the information of the image to be evaluated for quality evaluation. It has extremely high practical value and attracts more and more attention. However, natural images are rich in content and varied in noise. Existing evaluation models are difficult to accurately reflect image quality and can only be evaluated for specific noise. The application range is limited and the calculation complexity is high, which is difficult to meet the application needs.

Figure 2. The noise pollution image and the corresponding two-dimensional wavelet coefficient distribution in the TID2008 database
Statistical characteristic is the description quantity extracted from the statistical law peculiar to the natural image, and its characteristic will change with the change of the image noise pollution degree. The team studied the statistical characteristics of wavelet coefficients and found that the wavelet coefficients of low-noise or noise-free natural images have a distribution of fine peaks and spikes while noisy images are often flat-topped and have a shallower tail. According to the above rules, the kurtosis feature is designed to accurately describe the degree of image contamination by noise, a flexible regression model is constructed to fit a variety of noise types, and finally the fast overrun learning machine technology is used to extract the kurtosis of the extracted image wavelet coefficients. The statistical features are mapped to the image quality to complete the evaluation of the image quality to be detected. This work provides new ideas for achieving accurate and efficient image-free evaluation.
Link to the paper: https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2018.28 Attached to the author's introduction:
Deng Chenwei, professor and doctoral supervisor of School of Information and Electronics, BIT. In recent years, he mainly focused on the major national needs in the field of high-resolution ground observation, and carried out basic and applied research on intelligent real-time processing of remote sensing images. Published more than 30 SCI papers of the first/corresponding author, including three highly cited ESI papers, and more than 680 citations of five representative SCI papers. Compiled one book in Chinese and one in English. Relevant research results have been applied in specific fields, and won the second prize of Natural Science of China Electronics Society and the second prize of Military Science and Technology Progress.
Release Date:2020-04-30
Contribution:School of Information and Electronics
Editor:Cao Anqi
Audit:Si Liming
